Researchers at the Department of Human Genetics, Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, have reported a limited study for three probands showing that biallelic severe ABCA4 variants may be implicated in Early Onset Severe Retinal Dystrophy (EOSRD). The researchers proposed that ABCA4 and CNGB3 variants “could have an additive effect given the colocalization of the encoded proteins in cone photoreceptors cell membranes”. According to their data, the study expands “the phenotypic spectrum of disorders associated with variants in ABCA4 that now spans ages of onset between 0 and 80 years, with prominent roles for genetic or non-genetic modifiers”.
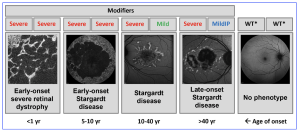
Figure 1. The spectrum of ABCA4 retinopathy. Representative FAF images are shown for each stage. Individuals with a normal fundus can carry any of these alleles: WT/WT, WT/severe, WT/mild, severe/mildIP, mild/mild, mild/mildIP, or mildIP/mildIP. MildIP, mild with incomplete penetrance; WT, wild type. Images were obtained and modified from Cremers FP et al, Prog Retin Eye Res. 2020;79:100861, (CC-BY license). [This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, cited by Panneman DM, et al. Expansion of the ABCA4-associated retinopathy spectrum: Severe variants can be associated with early-onset severe retinal dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025;66(6):19. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.66.6.19).
As a juvenile form of RP, LCA is a severe congenital or early infant-onset form of non-syndromic retinal disease characterised by severe retinal dystrophy, vision loss, nystagmus, an absence of a normal pupil response and an almost non-recordable ERG. LCA was originally identified by a German clinical ophthalmologist, Theodor von Leber in 1869 and the disorder was primarily based on the early infant-onset form of non-syndromic inherited visual loss. However, following the original description of the infantile disorder, a subsequent milder form of the same disease presented in the 6th and 7th years of life and led to blindness by the age of 30 years, considered to be on the same spectrum as LCA. This later-onset disease has been referenced by several different names including juvenile and early-onset retinitis pigmentosa, childhood-onset severe retinal dystrophy, Early Onset Severe Retinal Dystrophy (EOSRD) and Severe Early Childhood Onset Retinal Dystrophy (SECORD). A more recent structure for nomenclature, aiming to define the basis as being on genotype rather than phenotype (e.g., RPE65-related LCA), is preferable. Currently, the researchers studying in Nijmegen, investigated the genetic cause of disease and clinical characteristics in three probands with EOSRD.
The three patients were seen in various ocular genetics and retinal dystrophy clinics from Chicago, IL, USA, Vancouver, Quebec, Canada, and Auckland, New Zealand.
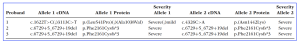
Table 1. Genetic Findings in ABCA4 for Probands 1, 2, and 3. Severity scores are according to Cornelis et al., Am J Hum Genet. 2022;109:498–507 The protein notation of the c.6729+5_6729+19del variant is based on the midigene assay results from Sangermano et al., Genome Res. 2018;28:100–110. [Open Access, Panneman DM, et al. Expansion of the ABCA4-associated retinopathy spectrum: Severe variants can be associated with early-onset severe retinal dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025;66(6):19. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.66.6.19)].
Following their analysis, the researchers described “a new genotype–phenotype correlation identified in three EOSRD probands that carry at least two severe variants in ABCA4”. The data showed that two probands carry the same pathogenic, homozygous splice site variant. In addition, extensive studies of the ABCA4 gene in associated conditions such as Stargardt disease (STGD1) and STGD-like macular diseases have revealed late-onset phenotypes, and they commented that “no link with severe early-onset IRDs such as EOSRD or LCA has been found previously”. Using whole genome sequencing (WGS), the researchers identified two NBAS (neuroblastoma-amplified sequence) variants and a homozygous CNGB3 (cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit beta 3) variant in probands 1 and 3, respectively. In summary, the team’s results “expand the phenotypic spectrum of disorders associated with variants in ABCA4”, spanning ages from birth to old age.