Researchers at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, USA and Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia, have reported a study on the most highly cited articles published in ophthalmic journals, as well as the ranking of journals, authors, institutions and countries. The study may be valuable “as a guide regarding contributions to the field”. The measure of the evaluation was conducted by the h-index, established in 2005, by Jorge E. Hirsch, a physicist in University California in San Diego. The measure aims to track both the scientific productivity and the apparent scientific impact of a scientists’ work. The h-index output may often correlate with success indicators in academe and medicine, including assessment in research fellowships, promotion in universities, employment or grant evaluations. While the h-index is well known and accepted by many researchers, it is not the only type of measurement on academic performance.
The h-index is based on the set of the researcher’s most cited papers and the number of citations that they have received in other people’s publications. While there can be a debate on which ways to measure research publications, the h-index is a reasonable representative measure of the average paper published in a given journal, rather than reflecting primarily the most popular paper or papers published in that journal. Hirsch himself has suggested that any given researcher, working after 20 years of research, an h-index of 20 is good, 40 is outstanding and 60 is truly exceptional. ~5,000 scholars around the world have an h-index >100, while the “top performer”, Dr. Ronald Kessler, a professor from Harvard working in psychiatry, has a h-index of 316 (as of March 2023 (https://www.webometrics.info/en/hlargerthan100)).
In the current report (Nichols et al., JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023;141(7):651-657), the h-index for ophthalmic journal articles was determined to be 494. The journal with the highest h-index was Ophthalmology (h-index, 297) and the journal with the greatest number of articles was American Journal of Ophthalmology (38,441 articles).
Table 1. Presented by Nichols et al., (2023), compiling 20 ophthalmic journals ranked by the h-Index [(a) Includes Archives of Ophthalmology; (b) Includes about 8000 abstracts; (c) Includes American Journal of Ophthalmology case reports; (d) Includes Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavia supplements.
The in the study, the most highly cited article was by Quigley and Broman, 2006 (5,147 citations), research on the epidemiology of glaucoma, while the author with the highest h-index for ophthalmic journal articles was Ronald Klein, MD (h-index, 126), working on epidemiology and the burden of visual impairment and blindness due to diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. The most prolific was Carol L. Shields, MD (1,400 articles) working in retinoblastoma and ocular melanoma.
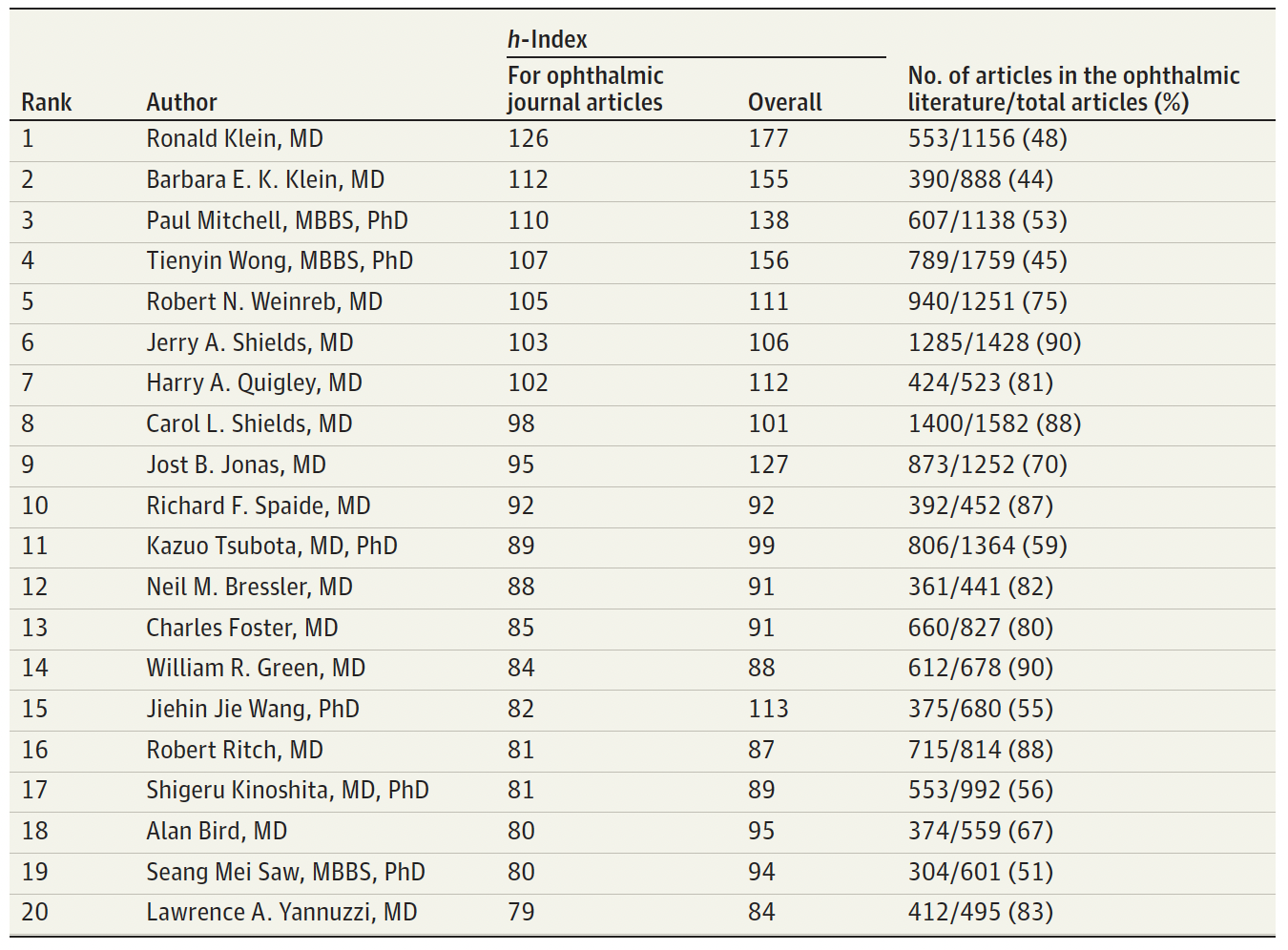
Table 2. Presented by Nichols et al., (2023), compiling the h-index authors publishing in ophthalmic journal articles.
According to the researchers, there are >18,000 refereed scientific articles per year are published in ophthalmic journals and these approximate to almost 50 articles per day. In concluding on the results, the authors commented that, “the combined h-index for ophthalmic journal articles of 494 can be compared with that of 10 arbitrarily selected medical fields by deriving crude estimates of the h-index of journal publications in each field. The h-indices of the disciplines represented range from 284 (hematology) to 714 (oncology), which places the ophthalmic journal literature in the middle of this ranking list. To our knowledge, this type of analysis has not been done previously in respect of other specialty medical journals.”
